In a globalized and networked economy, production interruptions, including the interruption of supply chains, have been the leading business risk for many years.
The ability of a company to permanently adapt to internal and external changes and disruptions is the „search for resilience“. Reinforced by a significant increase in complexity in production due to Industry 4.0, resilience management is thus becoming an indispensable success factor for production companies.
The SPAICER project develops a data-driven ecosystem based on life-long, collaborative and low-threshold Smart Resilience Services by using leading AI technologies and Industry 4.0 standards with the aim of anticipating disruptions (anticipation) and optimally adapting production planning to active disruptions at any time (response).



Video Statements
News
SPAICER Closing Event in Berlin
We are happy to announce that the closing event for SPAICER will be held at Spreespeicher in Berlin on June 23rd, 2023. You can register for the event here.
Objective

Malfunctions are omnipresent in production. They affect the supply of materials of insufficient quality, leakage of lubricant lines, damage to machines or tools, power failures or overloads and employee illness. Malfunctions can be foreseeable and unforeseeable. Disruptions often affect a company externally, such as systematic market changes in the form of innovative technologies (e.g. joint production lines or 3D printing), changes in demand patterns and supply chains or abrupt changes in political or financial systems. In addition, changes can also come from within, i.e. the products and production itself, such as their quality, branding and manufacturing (in)efficiency. In addition, there are changes in political regulation, the labour market and the environment. The ability of a company to permanently adapt to major internal and external changes and disruptions in complex, rapidly changing production networks is called the „search for resilience“.
In order to increase the resilience of individual production companies or entire production systems, disruptive potentials and trends in the market, network and company must be recognized early on, and an optimal response to acute disruptions must be made and learned from them. Thus, resilience is directly decisive for the competitiveness of a company. Companies that do not have sufficient resilience suffer considerable competitive disadvantages. The lower the effects of disruptions on production, the higher the resilience of a company. Due to a considerable increase in complexity in production caused by Industry 4.0, resilience optimization and resilience management is becoming an indispensable success factor in production companies.
The goal of the SPAICER research project is to develop a framework model and low-threshold, collaborative Smart Resilience Services to support AI-based resilience management for manufacturing companies in production systems. This enables companies to anticipate disruptions at an early stage and to react to any disruptions that occur in order to optimize production planning appropriately. The core of SPAICER is an agent-based, modular and open approach to the development of Smart Resilience Services, which are embedded in an ecosystem for the exchange of data, software and models based on leading AI technologies and industry 4.0 standards.
Solution approach:
In SPAICER, AI technologies are transformed into Smart Resilience Services (SRS) with a clear value proposition, integrated in production environments and networked with each other. To ensure the reusability of SRS and the exchange with partners (SRS ecosystems), platforms are developed and operated according to different „Industry 4.0“ standards on existing base platforms. To achieve this goal, (1) machine learning methods (ML) are particularly suitable for deriving forecasts and recommendations for action from data, and (2) formal planning and inference methods (PI) for the controlled application of structured knowledge. The combination of these two worlds is one of the most active areas of AI research. Since changes in production planning have far-reaching, entrepreneurial effects, they must be worked out interactively in collaborative environments together with production experts and decision-makers via natural language interfaces (Explainable AI). At the architectural level, SPAICER will investigate hybrid AI-oriented architectures, which distribute SRS to edge devices (including production machines) and cloud environments in an optimized way according to their performance and data protection requirements.
Use Cases

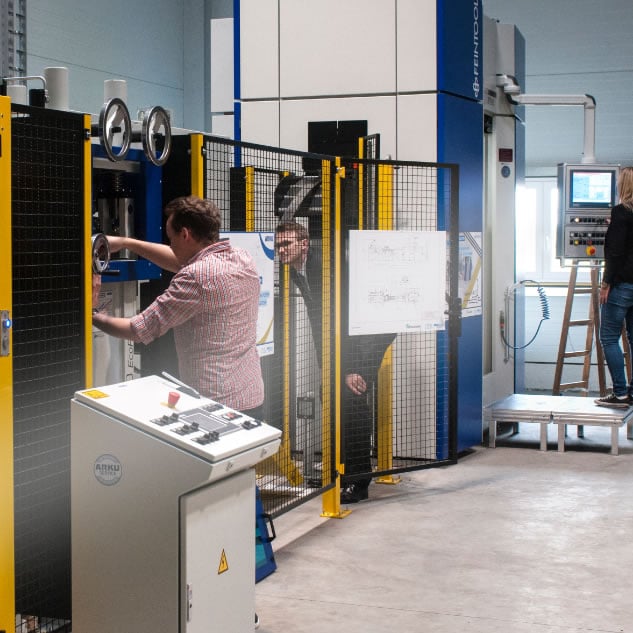
Use Case 1 „Self-optimization“
SPAICER enables manufacturing companies to classify disruptions on production lines and respond to them in real time. With the help of Smart Resilience Services (SRS), sensory data streams from production machines and quality data from tools and raw materials are analyzed, among other things. Based on this, recommendations for action can be given for parameter optimization, planning of maintenance intervals or precautionary termination of a production run. This enables a reduction in production errors due to machine wear as well as cost savings by avoiding production downtimes.
Two prototypes of Smarter Resilience Services in the manufacturing and process industries show how SPAICER enables non-destructive, digital material testing so that material wear can be reliably predicted and tool replacement or maintenance can be planned cost-effectively.

Use Case 3 „Knowledge transfer“
SPAICER enables manufacturing companies to continuously capture expert knowledge (colloquially known as „druid knowledge“) on the shopfloor. The knowledge gained can be made available to employees with a lack of know-how in the form of recommendations for action. Through the transfer of knowledge, problems in ongoing operations can be solved quickly despite the lack of experience of workers, and wrong decisions and additional costs can be avoided.

Use Case 4 „Proactive transformation“
Due to pandemics, political conflicts or speculation consumer markets can change or raw materials can become scarce. SPAICER provides companies with AI-based planning recommendations at an early stage. This enables decision-makers to assess whether it is worthwhile to build up reserves of raw materials or whether alternatives should be chosen, such as expanding the supplier network, increasing the order volume or spreading it over several locations.
Funding
Funding
by the Federal Ministry of Economic Affairs and Climate Action (BMWK) (funding reference 01MK20015A)

Funding within the AI innovation competition „Artificial intelligence as a driver for economically relevant ecosystems“.
Promoter
German Aerospace Center (DLR-PT) Promoter | Society, Innovation, Technology | Information Technologies/ Electric mobility
Volume
Approx. € 9.9 million
(thereof € 6.4 million funding by the Federal Ministry of Economic Affairs and Climate Action (BMWK), average funding rate: 64.6%)
Duration
01 April 2020 – 31 March 2023
Consortium
In addition to the German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI), which acts as coordinator, the Machine Tool Laboratory (WZL) at RWTH Aachen University, the University of Freiburg, the Technical University of Darmstadt, the Institute for Technology and Innovation Management at RWTH Aachen University, the Otto Beisheim School of Management (WHU), deZem, Feintool, SAP, SCHOTT, SEITEC, Deutsche Bahn AG, Mendritzki Gruppe and SENSEERING are involved in SPAICER.

Under the direction of Prof. Wolfgang Maaß, the Smart Service Engineering department at DFKI researches and develops AI-based services in production and manufacturing. The main focus is on distributed Smart Services, which are developed on the basis of Edge AI technologies. The German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI) GmbH as a whole was founded in 1988 as a non-profit public-private partnership (PPP). It has locations in Kaiserslautern, Saarbrücken, Bremen, Osnabrück, Oldenburg, a project office in Berlin and a branch office in St. Wendel. DFKI is Germany’s leading business-oriented research institution in the field of innovative software technologies based on artificial intelligence methods.

For more than 100 years, the Laboratory for Machine Tools and Production Engineering (WZL) of RWTH Aachen University has stood for pioneering research and successful innovations in the field of production technology worldwide. Under the direction of the four professors Christian Brecher, Thomas Bergs, Robert Schmitt and Günther Schuh, the WZL conducts research in six areas – production engineering, machine tools, production systems, gear technology, production measurement technology and quality management – to ensure that production in high-wage countries is future-oriented. Together with industrial partners from various sectors, the WZL develops solutions for a wide range of production issues in publicly funded and bilateral projects. These activities will be continued on the RWTH Aachen Campus in the Production Engineering Cluster.

The Institute for Technology and Innovation Management (TIME) at RWTH Aachen University conducts research on the topic of technology and innovation management from a strategic, behavioural and computational perspective. Under the direction of Prof. Frank Piller, extensive research has been conducted over the past decade in the areas of open innovation, co-creation and customer involvement in the innovation process, innovation culture, business model development and customer-oriented value creation. The institute is an integral part of the TIME Research Area at the Faculty of Economics at RWTH Aachen University.

The senseering GmbH (SE) is an AI and DLT start-up founded for the industrial production environment. SE realizes Industrial Internet of Things platforms with a focus on industrial goods, production plants, process technologies and logistics. With the help of hybrid edge and cloud computing approaches, (un)-supervised learning, data mining and machine learning methods are used to discover hidden patterns in industrial process data and feed them back into real-time controlled processes on an AI basis. SE’s expertise lies in particular in the digitization of industrial production plants (Operational Technology, OT), in building a bridge between the domain knowledge OT and IT (networking) and in the development of digital business models according to the zero-limit cost principle. In addition, a block-chain-based data marketplace, through which suppliers, participants and customers can exchange forgery-proof and encrypted data and order or use AI micro-services, increases the effectiveness of value-added networks in production to a new level. Thus, DFKI and SE complement each other in a special way.

WHU – Otto Beisheim School of Management is one of the best German business schools and enjoys a high national and international reputation. Founded in 1984 on the initiative of the Koblenz Chamber of Industry and Commerce as a university „by business for business“, WHU has become a role model for future-oriented research and teaching in the field of business administration. With the Kühne Institute for Logistics Management under the direction of Prof. Dr. Stefan Spinler, the areas of sustainability and risk management in supply chains and logistics networks are researched. In the context of sustainability, strategies for the reduction of CO2 emissions are developed and quantitatively evaluated using the real option methodology. This includes fleet modernization, trading of emission certificates and especially redesign of the supply chain network. WHU stands for „Excellence in Management Education“ and meets this demand in teaching, research and practice. The professional success of the graduates, the research results of the faculties and the profitable exchange with partners from the business world bear witness to this.

The Working Group for the Foundations of Artificial Intelligence (GKI) at the Institute for Computer Science of the Albert-Ludwigs-University of Freiburg (UniFr) is characterized by many years of experience with planning technologies. Theoretical research as well as the application of planning technologies to problems relevant in practice is in the foreground, among others in the fields of logistics and robotics (more recently e.g. within the cooperative BMBF project KARIS PRO as well as within the DFG Cluster of Excellence BrainLinks-Braintools and the DFG HYBRIS research group).

The TU Darmstadt (TuDa) contributes to the project its expertise in the field of artificial intelligence and machine learning. It is one of the leading technical universities in Germany. Prof. Dr. Kersting is head of the Department of Machine Learning at the TU Darmstadt and is one of the world’s leading researchers in the fields of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. For his achievements, he has been appointed European Association for Artificial Intelligence (EurAI) Fellow and has received several Best Paper Awards (TPM 2019, AIIDE2015m ECML 2006), the EurAI Dissertation Award for the best AI dissertation in Europe and a Fraunhofer ATTRACT Fellowship. He is (co-)editor of many flagship journals of AI and machine learning (AIJ, JAIR, MLJ, DAMI, Frontiers in Big Data) and has chaired important conferences such as the ECML PKDD and the UAI. Prof. Dr. Kersting is also a member of the BMBF platform „Learning Systems“ and initiator in the initiative Artifical Intelligence at TU Darmstadt (AIDA). The department „Machine Learning“ has extensive experience in projects. Prof. Kersting was involved in the IST FET projects APRIL I&II, the EU FP7 FIRST-MM project, 2 BMBF projects, three DFG projects (in SPP 1527 and SFB 876) and one GIF project and was head of the Fraunhofer ATTRACT group STREAM. In addition, several proposals (BMBF and LOEWE focus) in the field of Explanable Machine Learning and for a BMBF competence center for labour research in the field of Cooperative Machine Learning are currently being reviewed. Prof. Dr. Kersting will support SPAICER with his special expertise in the fields of statistical, relational and explanatory interactive learning.

SAP SE was founded in 1972 and is a global company with headquarters in Walldorf, Germany. It operates under the name SAP SE. SAP is the market leader for business software and the leading provider of analysis software and solutions for business intelligence. Worldwide, more than 77% of all transaction revenues are generated by an SAP system. With over 425,000 customers in more than 180 countries, the SAP Group has a global presence and employs more than 96,500 people, of whom around 18,500 work in Germany. SAP develops innovations that not only help customers optimize their workflows, but also improve the lives of people around the world through its integrated strategy. SAP enables its customers to positively influence the world economically, ecologically, and socially.

SEITEC GmbH has been developing and supplying complete solutions for industrial automation for over 20 years. In the context of Industry 4.0 it offers solutions for the digital transformation of components, machines or entire production lines. Together with their customers they develop their new digital business models based on leading iIoT platforms such as Siemens MindSphere. SEITEC GmbH starts with suitable consulting concepts, develops first Minimum Viable Products (MVP) and accompanies the customer up to the complete iIoT application. Finally, SEITEC offers its customers the complete service for the operation of applications on the iIoT platform. SEITEC GmbH is SIEMENS MindSphere Gold Partner and with its IoT spin-off seioTec GmbH is a member of Mindsphere World e.V. as an independent user association for new IoT business models.

deZem GmbH has been developing and distributing web-based software since 2003. This software is particularly useful for companies and public organizations that are characterized by a high and complex distributed consumption of energy and resources and can achieve significant optimizations in these areas. The focus is on the collection, visualization and analysis of relevant data as well as the support of the necessary processes with, if necessary, many different groups of participants. In addition to software, deZem also develops and distributes its own measuring instruments and versatile data loggers on a significant scale, partly as a white label for large partner companies. A comprehensive service program is also available to support both the field level and the most productive use of the software as required. The use of open protocols and general standards as well as the creation of additional data interfaces to connect already existing data sources are based on many years of experience and routine processes. In order to improve the processes of its industrial customers, deZem GmbH develops AI-based methods for anomaly detection and predictive maintenance.

SCHOTT AG is a leading international technology group in the fields of special glass and glass ceramics. With the experience of more than 130 years of outstanding development, material and technological expertise, the company offers a broad portfolio of high-quality products and intelligent solutions. This makes SCHOTT an innovative partner for many industries, such as household appliances, pharmaceuticals, electronics, optics, life sciences, automotive and aerospace. SCHOTT’s goal is for its products to become an important part of everyone’s life. The company focuses on innovation and sustainable success. SCHOTT AG has its headquarters in Mainz (Germany) and is wholly owned by the Carl-Zeiss-Stiftung. As a foundation company, SCHOTT assumes a special responsibility for its employees, society and the environment.

Feintool System Parts Jena GmbH is an internationally operating technology and market leader in fineblanking. As an innovation driver, Feintool is constantly expanding the boundaries of fineblanking and developing intelligent solutions for its customers‘ ideas. We realize the complete production of precision fineblanking and forming components in high volumes for demanding industrial applications. The processes used by Feintool System Parts Jena GmbH support the trends in the automotive industry. Founded in 1994 and based in Jena, Thuringia, the company currently employs 280 people and 9 apprentices. On ten highly automated production lines, approximately 110 million parts are manufactured for the automotive industry, with the main focus on transmissions.

Deutsche Bahn AG (DBAG) is a federally owned railroad group. The Group is subdivided into a number of companies, including DB Fernverkehr (long-distance passenger transport), DB Regio (local passenger transport) and DB Cargo (rail freight transport). The Group subsidiary DB Netz also operates large parts of the German rail infrastructure and thus the largest rail network in Europe. The company generates about half of its total sales in rail transport. he other half of the operating business is accounted for by the other transport and logistics business and various service providers. Deutsche Bahn AG is working intensively on the topics of digitalization and Industry 4.0. Industry 4.0. The „House of AI“ organizational unit is particularly worthy of mention here. The House of AI (DB AG) is a central point of contact for data use in the DB Group. Methodological competencies in the area of data analytics as well as machine learning and AI processes, including the application of Deep and Reinforcement Learning. The „House of AI“ is working on increasing transparency and networking in the overall rail system and to use the knowledge gained and methods for the and methods for integrating data and AI-based methods into processes across all business units. and make them usable. This is being achieved through a combination of a Group-wide governance and implementation function.

With more than 1,000 employees in Germany, France and China, the Mendritzki Gruppe develops and produces customer-specific solutions – from strip steel to ready-to-install components – for worldwide use in the automotive, industrial, agricultural and forestry sectors. With its nine plants, the companies of the Mendritzki Group are among the leading manufacturers in the business areas of precision strip steel, precision components and precision tools. Decades of experience, outstanding quality and maximum flexibility as well as forward-looking developments with partners from industry as well as research and development allow the company to meet the often special customer requirements.
In addition, SPAICER has a large, wide-ranging network of more than 40 associated partners who support the BMWi-funded consortium in the project and represent a complete value network in an exemplary manner. The associated partners without financial support participate in the project in a particularly early phase, are invited to all consortium meetings, and thus have the opportunity to actively participate and to gain exclusive, first insights into results and developments.